Softmax takes an N-dimensional vector as input and outputs an N-dimensional vector of probabilities which sums up to 1. It is a generalised version of logistic regression but with multi classes instead of two classes hence it can be used for multi-class classification.
Softmax equation: $$A = \frac{e^z}{\Sigma e^z}$$
The ground truth value for a softmax function is a one-hot encoded vector.
Cross-entropy loss
Cross entropy loss can be derived from the below expression.
$$ P(\frac{y}{x}) = \hat{y}^y(1-\hat{y})^{1-y}$$
We apply log on both sides
$$\log P(\frac{y}{x}) = \log \hat{y}^y + \underbrace{\log (1-\hat{y})}^{1-y}$$
We calculate the loss only when y = 1(ground truth value). So when y = 1 the second term in the above equations becomes zero and we are left with the first term. And as we want to define a loss function we would like to minimize it and hence we can place a negative symbol before the equation.
$$C.E.loss = -y\log \hat{y}$$
Backprop
Since softmax is a vector function we can’t just calculate the derivative of it. The derivatives will be another vector and we can use a Jacobian matrix for it.
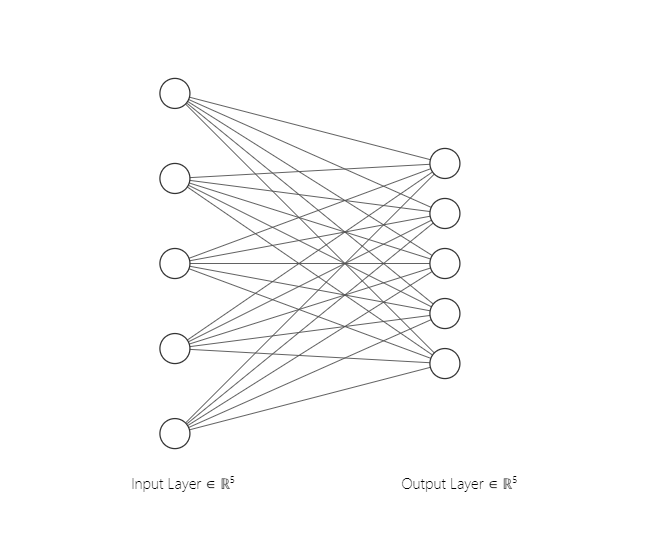
The above network is considered for backprop. The output layer is a softmax layer
Our final goal for back-propagation is to update weights and biases so we can minimize the loss. And to update the parameters with gradient descent we need the derivatives dL/dW and dL/db(Where L is the loss function, W, b are the weights and biases of the network). We calculate the two derivatives using the chain rule.
- L -> cross entropy loss
- W -> weights of the network
- b -> biases of the network
- A -> softmax activation function or $\hat{y}$
- z -> $wx + b$
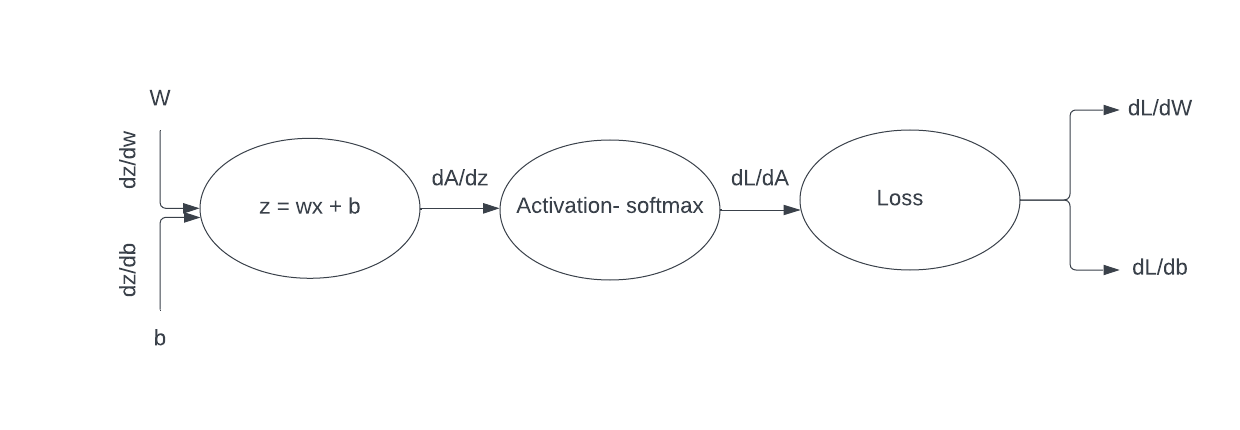
Chain rule for dL/dw and dL/db:
$$\frac{dL}{dW} = \frac{dL}{dA}.\frac{dA}{dz}.\frac{dz}{dw}$$
$$\frac{dL}{db} = \frac{dL}{dA}.\frac{dA}{dz}.\frac{dz}{db}$$
So we need to calculate $\frac{dL}{dA}$, $\frac{dA}{dz}$, $\frac{dz}{dw}$, $\frac{dz}{db}$.
- Calculating $\LARGE\frac{dL}{dA}$: $$L = -\Sigma {y_i}\log{A_i}$$
$$\frac{dL}{dA} = -\Sigma\frac{y_i}{A_i}$$
Calculating $\LARGE\frac{dA}{dz}$:
Consider the activation of ith neuron. Then we have two cases where we consider the ith dz or jth dz.
when i = j: $$\frac{A_i}{z_i} = \frac{e^{z_i}}{\Sigma e^{z_i}}$$
$$\frac{dA_i}{dz_i} = \frac{e^{z_i}(\Sigma e^{z_i})-(e^{z_i})^2}{(\Sigma e^{z_i})^2}$$
$$\frac{dA_i}{dz_i} = A_i(1-A_i)$$
- when i $\not =$ j:
$$\frac{dA_i}{dz_j} = \frac{0-e^{z_i}e^{z_j}}{(\Sigma e^z)^2}$$
$$\frac{dA_i}{dz_j} = -A_iA_j$$
- Calculating $\LARGE{\frac{dz}{dw}, \frac{dz}{db}}$:
$$z = wx + b$$ $$\frac{dz}{dw} = x$$ $$\frac{dz}{db} = 1$$
Calculating $\LARGE\frac{dL}{dz}$: $$\frac{dL}{dz} = \frac{dL}{dA}.\frac{dA}{dz}$$ $$\frac{dL}{dz} = - \Sigma\frac{y_i}{A_i}.\frac{dA}{dz}$$ $$\frac{dL}{dz}= -\frac{y_i}{A_i}.\frac{dA_i}{dz_i}- \Sigma\frac{y_j}{A_j}.\frac{dA_i}{dz_j}$$
- substituting the above da/dz values: $$\frac{dL}{dz} = -\frac{y_i}{A_i}.{A_i}(1-{A_i})- \Sigma\frac{y_j}{A_j}.(-{A_i}{A_j})$$
$$= - {y_i} + {y_i}{A_i} + \Sigma{y_j}{A_i}$$ $$= - {y_i} + {y_i}{A_i} + {A_i}\Sigma{y_j}$$ $$= - {y_i} + A_i\Sigma y$$ $$\frac{dL}{dz}= A_i - y_i$$
Calculating $\LARGE\frac{dL}{dw}$: $$\frac{dL}{dw} = \frac{dL}{dz}.\frac{dz}{dw}$$ $$\frac{dL}{dw} = X(A_i - y_i)$$
Calculating $\LARGE\frac{dL}{db}$: $$\frac{dL}{db} = \frac{dL}{dz}.\frac{dz}{db}$$ $$\frac{dL}{db} = A_i - y_i$$
Code
import numpy as np
def softmax(z):
a = np.exp(z)
a = a/np.sum(a, axis = 0, keepdims=True)
return a
def init_parameters():
w = np.random.randn(1, 5)*10
b = np.zeros(5)
return w, b
def cross_entropy_loss(A, y):
loss = -np.mean(y*np.log(A))
return loss
def forward(w, X, b):
z = np.dot(X, w.T) + b
A = softmax(z)
return A
def backprop(A, X, y, w, b, alpha):
dz = A - y
print('dz: ', dz)
print(X)
dw = dz*X
db = A - y
print('dw: ', dw)
w = w - alpha*dw
b = b - alpha*db
return w, b
alpha = 0.7
X = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
y = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1])
w, b = init_parameters()
print('initial w, b: ', w, b)
A = forward(w, X, b)
print('A: ', A)
w, b = backprop(A, X, y, w, b, alpha)
print('after backprop: ', w, b)
References
[1] https://eli.thegreenplace.net/2016/the-softmax-function-and-its-derivative/